- Intelligent Automation
- Written By Namita Bhagat
The Business Automation Outlook 2026: What’s Shifting and Why It Matters
24-Dec-2025 . 8 min read
The Business Automation Outlook for 2026 highlights a pivotal shift. Automation is no longer just a back-office efficiency tool. It has become a strategic engine guiding how businesses adapt, scale, and grow. Today, business leaders increasingly recognize that automation shapes more than task execution. It influences how operating models respond to disruption and capture new opportunities.
This article explores key trends, signals, and strategic changes reshaping the automation landscape. And it offers you a grounded view of what it means for organizations and workplaces!
Business Automation Evolution & Learning Curve
The conversation around automation in business is maturing. No more just a tactical lever for efficiency and cost reduction, process automation initiatives are now a premeditated enabler of operational agility, scalability, and resilience.
Should we automate?” is given. Instead, attention has shifted to questions around:
- How do we align automation with our business model?
- How do we scale automation across departments and functions?
- How do we govern our automations and AI responsibly?
Today, business process automation is moving towards:
- Orchestrating end-to-end workflows, not just automating tasks
- Empowering teams with AI-powered automation systems
- Building operational muscle memory that adapts to change
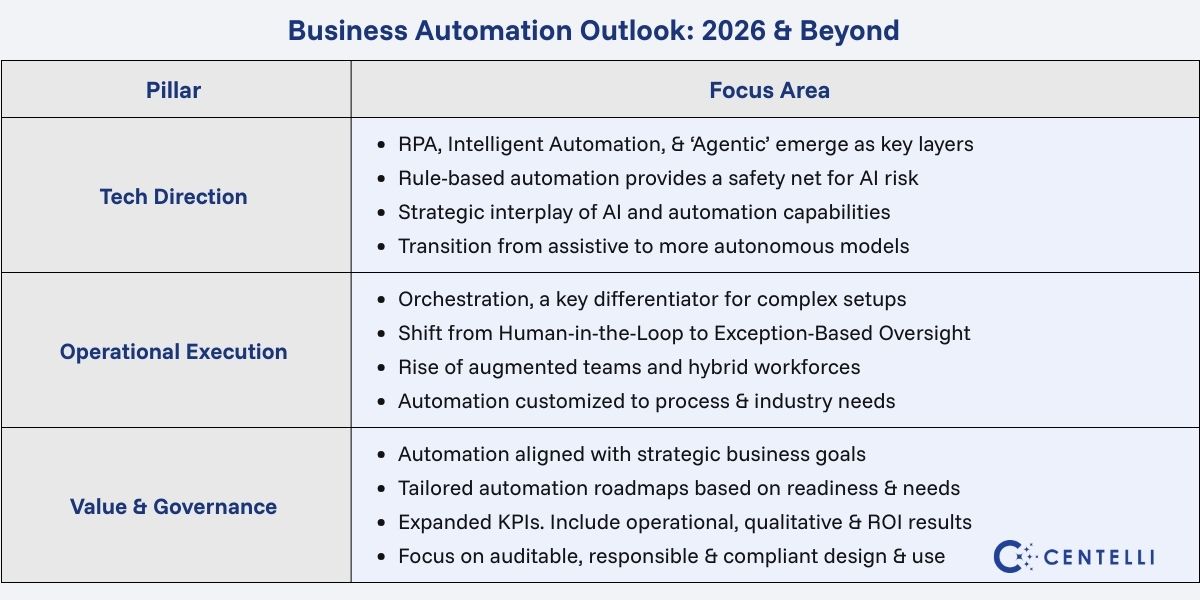
Business Automation Outlook 2026 & Beyond
To understand where Business Process Automation (BPA) is heading, we must look beyond tools. The real shift is in how the automation landscape itself is evolving. This is not just about technology trends—it’s about rethinking solution design, governance models, deployment strategies, and how performance is measured.
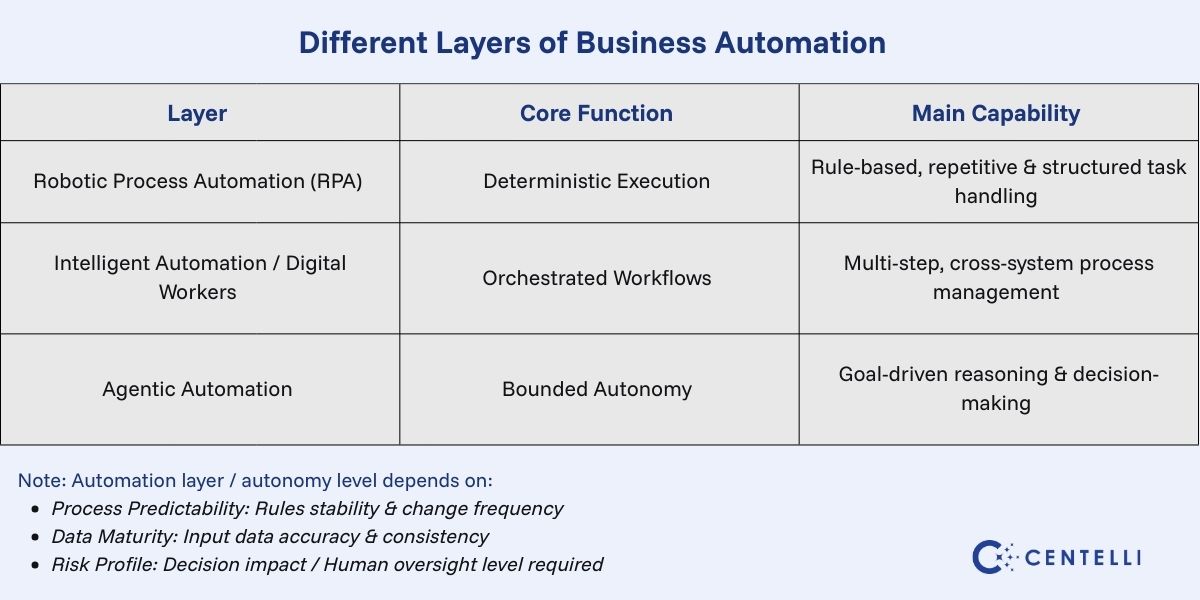
Automation Layers Are Consolidating, Not Competing
Business automation in 2026 is no longer about choosing between tools. Instead, it’s about stacking capabilities:
- RPA handles deterministic, rule-based execution
- Digital workers and intelligent automation manage multi-step, cross-system workflows
- Agentic automation introduces autonomy within defined boundaries
These layers are complementary rather than rivals. As a result, the most effective automation strategies combine them into a coherent operating model rather than deploying them in isolation.
Human-in-the-Loop to Exception-Based Oversight
Many organizations rely on human-in-the-loop (HITL) controls to manage AI risk. In regulated or high-stakes scenarios especially, this caution is both necessary and appropriate.
However, when humans are required to review every decision, HITL can slow automation without materially improving outcomes, particularly in high-volume, low-risk processes. This model is gradually evolving.
Organizations are shifting to exception-based oversight:
- Where automation handles entire task / process without human oversight
- Humans intervene only when predefined risk thresholds are breached or ambiguity arises.
Consequently, this creates human-on-the-loop (HOTL), an extended version of automation operation. It preserves human judgment where it matters most while allowing automation to scale responsibly. However, there could be high risk and high compliance situations where human-in-the-loop is non-negotiable.
Orchestration Becomes a Key Differentiator
Moving ahead, the most critical automation decision won’t be which tool you deploy — it will be how well you orchestrate across tools and systems. This applies to mid to large organizations. Many will need a unified automation framework that can:
- Coordinate RPA bots, AI agents, and human teams
- Enforce governance and escalation rules consistently
- Monitor performance, risk, and outcomes in real time
Ultimately, automation ripeness will be defined less by individual capabilities and more by the orchestration layer that holds everything together.
Need an expert assessment of your automation maturity and readiness to scale? Or want our help with early-stage automation initiatives? Get started with a free consultation today.
Aligning Process Automation with Business Impact
Efficiency and productivity are no longer the sole criteria for automation initiative success. The focus has shifted to strategic value, measurable outcomes, and sustainable impact. Businesses now expect automation that accelerates processes, strengthens decision-making, enhances experiences, and builds operational resilience.
Why it matters: Initiatives must do more than impress on paper. They need to connect automation to tangible business metrics, integrate across teams and systems, and maintain transparency and governance.
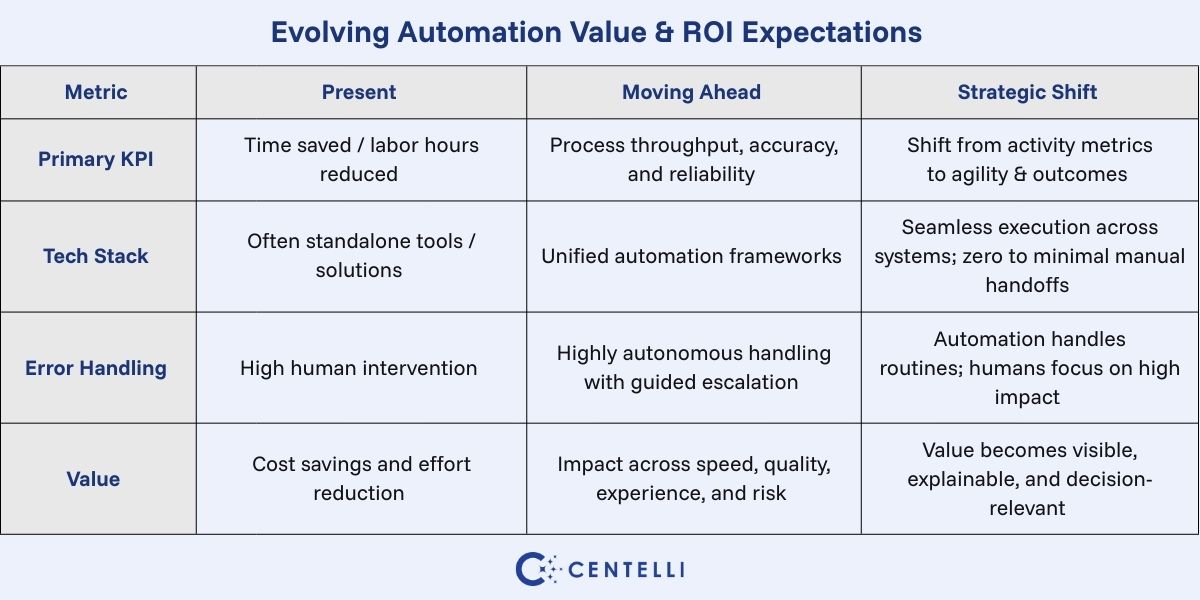
Goals, KPIs & ROI: Measuring What Really Matters
The definition of automation success is expanding as mentioned. It’s no longer just about time saved or FTEs reduced. In the coming future, the success will also be measured in terms of:
- Decision velocity i.e. how quickly insights turn into action
- Process resilience i.e. how well workflows adapt to change
- Experience impact i.e. how automation improves employee & customer journeys
Why it matters: ROI is being redefined. Success is measured by outcome-based metrics that reflect strategic value, not just operational efficiency. And that includes qualitative results as well.
AI + Automation: A Strategic Collaboration
We are moving toward a model where AI suggests creative solutions while business rules decide the final execution. AI and Automation together enable businesses to navigate stricter global data privacy and automation compliance regulations.
The key themes emerging in 2026:
- The ‘Hybrid Intelligence’ trend will become stronger
- Integrated automation becomes the primary vehicle for Responsible AI
- Human oversight remains a critical safeguard in high stake environment
Why it matters: Automation provides a safety net in an AI-hype world, ensuring business continuity even when AI stumbles.
Business Size & Maturity: Tailored Process Automation Roadmap
some SMBs are scaling through low-code automation. While cost-effective, the deployment can be susceptible to security vulnerabilities. so, it’s better to hire solution experts that prioritize security and governance by design.
Meanwhile, mid-market firms are untangling fragmented automation stacks, and enterprises are consolidating platforms while embedding automation into core systems. The journey differs, but the destination is shared: scalable, sustainable automation.
Why it matters: There’s no one-size-fits-all roadmap. Automation strategies must align with organizational maturity level, not just ambition.
Process & Sector Priorities: Where Automation Is Headed
Automation is shifting from tasks to end-to-end journeys. Imagine work flowing from invoice processing to onboarding, and from compliance to customer service. Banking and finance, e-commerce/retail, and supply chain sectors are early adopters. The phenomenon is picking up in hospitality and travel, healthcare, manufacturing, and many other sectors.
Why it matters: Automation models and AI are opening opportunities for scale and growth without adding overhead. This is especially valuable in businesses with high task volumes and talent shortages.
Workforce Dynamics: The Rise of the Augmented Team
Automation isn’t replacing people — it’s reshaping roles. Employees now work alongside digital workers, AI agents, and automated workflows. Cross-functional teams leverage technology to make faster, smarter decisions.
- Easy-to-use solutions don’t require deep technical knowledge.
- A bit of training is enough to get teams productive and confident with automation.
Why it matters: The future of work is collaborative, augmented, and automation-literate.
Innovation & Stakeholder Mindset: From Experimentation to Expectation
Innovation used to be a side project; now, it’s a survival and growth strategy. This means:
- Stakeholders expect measurable value, not just pilots.
- Automation is no longer a tech initiative — it’s a business imperative.
Why it matters: Organizations are seeing value in moving away from “trying automation” to scaling it with purpose.
25 Business Processes Where Automation Scope is Widening
Following are 25 high-impact business processes where automation is gaining strong traction. The choice between RPA, digital workers, intelligent automation, hyperautomation, or agentic automation depends on the specific process needs and use cases, however.
Processes with Rapid Automation Adoption
- Employee Lifecycle Automation
Automates onboarding, role changes, compliance training, and secure offboarding. - Customer Identity Verification (eKYC)
Uses OCR, facial recognition, and fraud detection to streamline onboarding and compliance. - Contract Lifecycle Management (CLM)
Automates clause extraction, redlining, approvals, and renewal tracking. - Procure-to-Pay (P2P) & Vendor Management
Streamlines requisitions, approvals, invoice matching, and vendor onboarding. - Customer Sentiment Routing
Uses NLP to analyze and route feedback to the right teams. - Warranty Claims Processing
Automates eligibility checks, document validation, and approvals. - Internal Audit Preparation
Prepares audit-ready documentation, control testing, and evidence collection. - Board Reporting & Executive Dashboards
Automates data consolidation and formatting for board-ready reports and real-time leadership insights. - Subscription & Billing Management
Automates renewals, usage tracking, invoicing, and failed payment recovery for recurring revenue models.
Processes Where Automation Is Gaining Momentum
- Vendor Risk Monitoring
Scans for financial, geopolitical, and ESG risks using internal and external data. - Regulatory Intelligence Monitoring
Tracks global policy changes and flags relevant updates. - Sustainability Compliance Checks
Tracks emissions, waste, and sustainability KPIs. - ESG Data Aggregation & Reporting
Consolidates ESG metrics for investor and regulatory reporting. - Partner Onboarding & Due Diligence
Automates background checks, compliance screening, and contract workflows. - Rebate & Incentive Management
Validates eligibility, automates calculations, and processes payouts. - Incident Response & Escalation Workflows
Triggers automated triage, escalation, and resolution protocols for IT, security, or operational incidents. - Diversity & Inclusion Metrics Tracking
Aggregates DEI data across hiring, promotion, and retention. - Budget (CapEx) Planning & Processing
Streamlines CapEx approvals, budget validation, and documentation workflows for faster investment decisions.
Sector-Specific and Advanced Use Cases
- Field Service Dispatch Optimization
Coordinates technician scheduling, routing, and inventory allocation. - Franchisee Support Operations
Automates ticket triage, compliance checks, and resource provisioning. - Knowledge Base Curation
Auto-tags, summarizes, and updates internal documentation. - Product Lifecycle Change Management
Automates engineering change orders and stakeholder notifications. - Digital Twin Synchronization
Keeps digital replicas of physical assets updated in real time. - Clinical Trial Data Validation
Automates data integrity checks and protocol compliance. - Intellectual Property (IP) Docketing
Tracks patent and trademark deadlines and renewals.
[The list is only illustrative. The length and breadth of use cases can be wider)
Two Notable Enterprise Automation Outlooks in 2026
Importantly, the automation themes highlighted here do not remove people from the equation. Instead, they change where and when human intervention occurs.
This is how it may look like:
- Automation takes ownership of routine execution and structured decision pathways
- AI serves as the cognitive engine for unstructured data & complex variables in real time
- Humans move upstream into design, oversight, and exception handling.
1. From Assistive to More Autonomous Automation
So far, automation largely played a supporting role. For example: reducing manual effort, helping teams to complete tasks faster, and improve efficiency at the margins. Going forward, this assistive phase will provide a clear foundation rather than the end state.
More autonomous approach means:
- Systems can execute, decide, escalate, and recover with minimal human involvement.
- They operate within defined guardrails, applying rules, policies, and context-aware logic
- This allows automations to manage variability at scale
The shift will be increasingly prominent among businesses that have already stabilized core automation programs and governance models.
2. Rule-Based Automation Matters in an AI-led World
As AI capabilities accelerate, it is easy to assume that rules-based automation is becoming obsolete. Interestingly, the opposite is true: rule-based automations remain a critical pillar of enterprise-level AI-powered automation initiatives.
Here’s why:
- Predictability: In regulated and mission-critical environments, deterministic outcomes are non-negotiable. Rules ensure consistency where variability introduces risk.
- Auditability: Rule-based logic is transparent, traceable, and explainable — essential for audits, compliance reviews, and regulatory reporting.
- Resilience: When AI models drift, fail, or hallucinate, rule-based automation provides a reliable fallback that keeps processes running.
Hybrid model = AI + rules, ensuring innovation doesn’t compromise control.
Key Takeaways for Business Leaders
The future of business automation is unmistakable: it is strategic, connected, and indispensable. To achieve meaningful outcomes in this evolving landscape, you need to:
- Reframe automation as a capability builder, not a cost cutter
- Align automation with business model evolution
- Thoughtful design: AI where it fits, automate where it matters
- Build governance frameworks that are easy to scale
- Set up continuous monitoring and performance loops
Ready to embrace the emerging landscape and make the most of it? Speak to Centelli to learn how our deeply strategic automation blueprint and custom solutions help you navigate and stay ahead.




